Plant sap analysis represents a significant advancement in agricultural nutrient management
Rapid technological advancements and a shift toward precision farming are reshaping the agricultural landscape. Within this context, plant sap analysis has emerged as a tool that offers real-time insights into the nutritional status of crops.
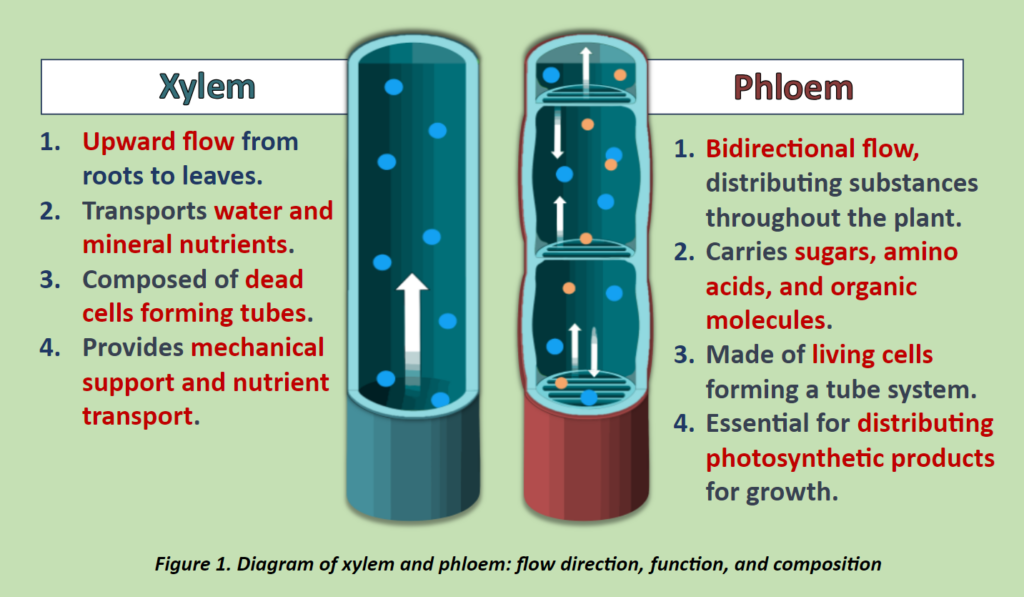
However, comprehending the full potential of plant sap analysis goes beyond just appreciating its technological prowess. It requires an in-depth understanding of plant physiology, especially the roles of xylem and phloem and their functional variations across different plant parts. The xylem, specifically in roots, plays a vital role in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil (Figure 1).
In contrast, the phloem, distributed throughout the plant, is responsible for transporting synthesized nutrients essential for growth, energy and storage. In stems, xylem facilitates water transport and provides structural support, whereas phloem manages nutrient and hormone distribution. In leaves, these systems support photosynthesis and the distribution of sugars (Figure 1 & 2). Recognizing the unidirectional function of xylem and the multidirectional capability of phloem is essential.
Support authors and subscribe to content
This is premium stuff. Subscribe to read the entire article.